ANTIBIOTICO RESISTENZA
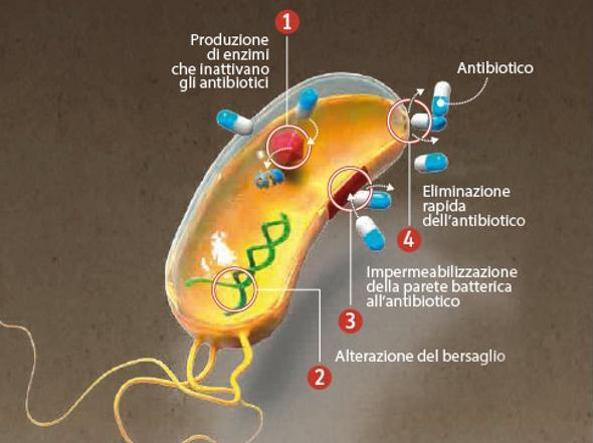
Antibiotic resistance: Latest results from PubMed
-
Re-evaluating what makes a phage unsuitable for therapy
One of the biggest challenges in phage therapy is selecting the 'right' phage. What constitutes a 'good' phage is unclear, but regulators are converging on exclusion criteria for 'bad' phages. Here, we examine three commonly applied criteria: the lack of virulence/antibiotic resistance, the inability to transduce, and being strictly lytic (virulent). We assess the risk posed, the tools for determining the criteria, and the potential impact of the criteria. -
Anti-urease therapy: a targeted approach to mitigating antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori while preserving the gut microflora
The global rise in antibiotic resistance has posed significant challenges to the effective management of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), a gastric pathogen linked to chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancer. Conventional antibiotic therapies, while effective, face significant challenges, such as increasing antibiotic resistance, high recurrence rates, and adverse effects such as gut microflora dysbiosis. These limitations have driven the exploration of alternative antibiotic-free... -
The neglected model validation of antimicrobial resistance transmission models - a systematic review
CONCLUSION: Despite efforts to model antimicrobial resistance and prevention strategies, significant gaps in scope, geographical coverage, drug-pathogen combinations, and viral-bacterial dynamics persist, along with inadequate documentation, hindering model updates and consistent outcomes for policymakers. This review highlights the need for robust modelling practices to enable model refinement as new data becomes available. Particularly, new data for validating modelling outcomes should be a... -
Role of bestatin as a treatment for periodontitis
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease impacting the supporting structures of teeth, with significant global pervasiveness and systemic health implications. Current treatments, such as scaling and root planning (SRP) and adjunctive antibiotics, face challenges including antibiotic resistance, infection recurrence, and incomplete tissue regeneration. Bestatin, a dipeptide aminopeptidase inhibitor, has shown potential as a novel therapeutic agent due to its targeted antimicrobial effects... -
Discharging Patients With Pending Microbiology Cultures: A Narrative Review of Safety and Best Practices
Discharging patients with pending microbiology culture results from the hospital has become a common practice aimed at improving hospital throughput and reducing length of stay. One of the main contributors to prolonged hospitalization is the delay in receiving finalized culture results, especially when patients are clinically stable and ready for discharge. Consequently, many hospitals have explored strategies to safely discharge patients before culture results are finalized. While this... -
Helicobacter pylori Vaccine: Mechanism of Pathogenesis, Immune Evasion and Analysis of Vaccine Types
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a gram-negative, spiral-shaped bacterium that colonizes the human gastric mucosa, leading to various gastric diseases. H. pylori infection has become a pressing public health issue that affects more than 50% of the human population worldwide, almost 40 years after its discovery. Traditional treatments, based on the use of bismuth-based triple and quadruple therapies, are effective while facing a series of problems, such as difficulty in patient compliance, the... -
Evolution of Antiviral Drug Resistance in SARS-CoV-2
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact and continues to alarm the entire world due to the rapid emergence of new variants, even after mass vaccinations. There is still an urgent need for new antivirals or strategies to combat the SARS-CoV-2 infections; however, we have success stories with nirmatrelvir. Drug repurposing and drug discovery may lead to a successful SARS-CoV-2 antiviral; however, rapid drug use may cause unexpected mutations and antiviral drug resistance. Conversely,... -
The Need for the Optimization of HIV Antiretroviral Therapy in Kazakhstan
The number of people living with HIV in Kazakhstan increased from 11,000 to 35,000 between 2010 and 2021, with emerging antiretroviral therapy (ART) resistance posing a challenge to effective treatment. Unsafe injection practices among people who inject drugs (PWID), the stigma against men who have sex with men, sex work, drug possession, HIV transmission, HIV exposure, and the non-disclosure of HIV status create obstacles to effective prevention and care. Our recent studies with people living... -
Casein and Casein-Derived Peptides: Antibacterial Activities and Applications in Health and Food Systems
The growing threat of antimicrobial resistance has intensified the search for alternative strategies to conventional antibiotics and preservatives. Casein-derived antimicrobial peptides (CDAMPs), generated through proteolysis, exhibit potent activity against a broad spectrum of pathogens, including antibiotic-resistant strains, revealing strong potential as natural preservatives and therapeutic agents in food and medical applications. Furthermore, casein can be an ideal source for peptide... -
Characterization of Antibiotic Resistance in Shewanella Species: An Emerging Pathogen in Clinical and Environmental Settings
Antibiotic resistance is increasing at an alarming rate worldwide, in large part due to their misuse and improper disposal. Antibiotics administered to treat human and animal diseases, including feed supplements for the treatment or prevention of disease in farm animals, have contributed greatly to the emergence of a multitude of antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Shewanella is one of many bacteria that have developed antibiotic resistance, and in some species, multiple-antibiotic resistance (MAR).... -
Review of the Presence and Phage-Mediated Transfer of ARGs in Biofilms
The widespread use of antibiotics has led to the emergence of a large number of drug-resistant bacteria, accelerating the dissemination and spread of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in the environment. Bacterial biofilms, serving as reservoirs of ARGs, pose potential risks to environmental health that should not be ignored. Studies on the presence and transfer of ARGs in biofilms have been conducted both domestically and internationally. This article summarises the research progress on ARGs... -
Prevalence of Colistin-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates in Turkey over a 20-Year Period: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Klebsiella pneumoniae is one of the leading causes of healthcare-associated infections and poses challenges in its treatment owing to its high antibiotic resistance. The development of resistance to colistin, which is used as a last resort, has become a major public health problem worldwide. This study was planned according to the PRISMA guidelines and included studies reporting the prevalence of colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae in Turkey between 2004 and 2024 through a systematic literature... -
Antimicrobial Resistant Staphylococcus spp., Escherichia coli, and Salmonella spp. in Food Handlers: A Global Review of Persistence, Transmission, and Mitigation Challenges
Antimicrobial resistance in foodborne pathogens represents a critical global health challenge, with food handlers serving as key contributors in their transmission. This comprehensive review synthesizes evidence on the prevalence, transmission dynamics, and antimicrobial resistance patterns of three major pathogens, Staphylococcus spp., Escherichia coli, and Salmonella spp., among food handlers worldwide. Analysis of studies across diverse geographical regions reveals considerable variation in... -
Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Insights into Virulence, Antibiotic Resistance, and Fight Strategies Against a Superbug
Community-acquired infections caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) have become a significant global health concern, particularly with the emergence of hypervirulent strains (hvKP). These strains are associated with severe infections, such as pyogenic liver abscesses, even in otherwise healthy individuals. Initially reported in Taiwan in the 1980s, hvKP has now spread worldwide. The pathogenicity of hvKP is attributed to an array of virulence factors that enhance its ability to... -
Recent Developments in Penem Antibiotics: Structural and Therapeutic Perspectives
This review examines the latest progress of β-lactam antibiotics, focusing on penems. Penems are distinguished by their unique structural characteristics and remarkable antibacterial activity. The structural characteristics of the class that differentiate it from carbapenems or monobactams are addressed. Notable representatives such as sulopenem and faropenem are discussed. Faropenem's stability and efficacy against resistant bacterial strains emphasize the therapeutic potential of penems. The... -
Insights on the Pathogenesis of Mycobacterium abscessus Infection in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis
People with CF (pwCF) have a significant risk for pulmonary infections with non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM), particularly Mycobacterium abscessus (Mab). Mab is an emerging pathogen, which causes pulmonary infections in patients with chronic lung diseases, particularly CF; Mab pulmonary disease leads to progressive pulmonary dysfunction and increased morbidity and mortality. Despite advances in CF care, including CFTR modulators (CFTRm), Mab continues to pose a therapeutic challenge, with... -
Medical Potential of Insect Symbionts
Insect symbionts and their metabolites are complex and diverse and are gradually becoming an important source of new medical materials. Some culturable symbionts from insects produce a variety of active compounds with medical potential. Among them, fatty acids, antibacterial peptides, polyene macrolides, alkaloids, and roseoflavin can inhibit the growth of human pathogenic bacteria and fungi; lipases, yeast killer toxins, reactive oxygen species, pyridines, polyethers, macrotetrolide nactins,... -
Probiotic, Prebiotic, and Synbiotic Supplementation for the Prevention and Treatment of Acute Otitis Media: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
CONCLUSIONS: Supplementation with probiotics, prebiotics, or synbiotics is associated with a significant reduction in the incidence of AOM in children, although no significant impact was observed on other key clinical parameters. These interventions may be considered as a complementary strategy to conventional treatments; however, further high-quality, standardized trials are needed to confirm these findings and to define optimal protocols. -
Combatting Pseudomonas aeruginosa with β-Lactam Antibiotics: A Revived Weapon?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a significant threat to public health as an aggressive, opportunistic pathogen. The use of β-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, and carbapenems remains a front-line treatment against P. aeruginosa. However, the widespread use of β-lactams has led to the emergence of β-lactam-resistant isolates that significantly increase the economic burden and risk of mortality in patients. With the declining productivity of the antibiotic discovery... -
Helicobacter pylori Antibiotic Resistance in Russia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Objective: This systematic review and meta-analysis aims to evaluate the temporal changes in Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance in Russia based on studies published over the past 15 years. Materials and Methods: We conducted a comprehensive literature search in MEDLINE/PubMed, EMBASE, the Russian Science Citation Index, and Google Scholar, following the PRISMA 2020 guidelines. Our meta-analysis was pre-registered in PROSPERO (CRD 420251025636). The inclusion criteria included original... -
The Antimicrobial Efficacy of Copper Complexes: A Review
The alarming increase in antimicrobial resistance has intensified the search for novel therapeutic agents capable of combating resistant microbial strains. Copper complexes have emerged as promising antimicrobial agents due to their intrinsic redox activity, ability to disrupt microbial membranes, and interactions with vital biomolecules such as DNA and proteins. This review critically evaluates the antimicrobial potential of copper complexes reported between 2018 and 2025, emphasizing their... -
One Health at Risk: Plasmid-Mediated Spread of mcr-1 Across Clinical, Agricultural, and Environmental Ecosystems
The global dissemination of plasmid-mediated mcr genes, which confer resistance to the last-resort antibiotic colistin, represents a critical public health challenge driven by the interplay of clinical, agricultural, and environmental factors. This review examines the genetic and ecological dynamics of mcr-bearing plasmids, focusing on their role in disseminating colistin resistance across diverse bacterial hosts and ecosystems. Key plasmid families demonstrate distinct evolutionary strategies,... -
Essential Oils for Biofilm Control: Mechanisms, Synergies, and Translational Challenges in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance
Biofilms, structured microbial consortia embedded in self-produced extracellular matrices, pose significant challenges across the medical, industrial, and environmental sectors due to their resistance to antimicrobial therapies and ability to evade the immune system. Their resilience is driven by multifaceted mechanisms, including matrix-mediated drug sequestration, metabolic dormancy, and quorum sensing (QS)-regulated virulence, which collectively sustain persistent infections and contribute to... -
Clinical Effectiveness of Penicillin-Free Therapies in First-Line and Rescue Treatments for Helicobacter pylori: A Systematic Review
Background and Aims: Amoxicillin is one of the most effective antibiotics for treating Helicobacter pylori infections and is widely used in first-line treatment regimens. However, patients with penicillin allergies cannot receive penicillin-based therapies, which significantly limits effective eradication options. This allergy often compels clinicians to choose alternative regimens that may be less effective, thereby increasing the risk of treatment failure. Consequently, therapeutic options for... -
Staphylococcus aureus: A Review of the Pathogenesis and Virulence Mechanisms
Staphylococcus aureus is a formidable human pathogen responsible for infections ranging from superficial skin lesions to life-threatening systemic diseases. This review synthesizes current knowledge on its pathogenesis, emphasizing colonization dynamics, virulence mechanisms, biofilm formation, and antibiotic resistance. By analyzing studies from PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, we highlight the pathogen's adaptability, driven by surface adhesins (e.g., ClfB, SasG), secreted toxins (e.g.,... -
Antibiotic De-Escalation in the Intensive Care Unit: Rationale and Potential Strategies
Antibiotic de-escalation (ADE) is important to help optimize antibiotic use and balance the positive and negative effects of antimicrobial therapy. ADE should be performed promptly, and infections should be treated with the shortest course of antimicrobials as clinically feasible to avoid unnecessary use of broad-spectrum antimicrobials. Several tools have been developed to increase efficient ADE, including rapid diagnostic tests (ex. multiplex PCR), MRSA nasal PCR/culture, and biomarkers.... -
Overcoming Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Chronic Suppurative Lung Disease: Prevalence, Treatment Challenges, and the Promise of Bacteriophage Therapy
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a multidrug-resistant pathogen, significantly impacts patients with chronic respiratory conditions like cystic fibrosis (CF) and non-CF chronic suppurative lung disease (CSLD), contributing to progressive lung damage and poor clinical outcomes. This bacterium thrives in the airway environments of individuals with impaired mucociliary clearance, leading to persistent infections and increased morbidity and mortality. Despite advancements in management of these conditions,... -
Leveraging Hospital Information Data for Effective Antibiotic Stewardship
Clinical informatics has emerged as a valuable approach to enhance antimicrobial stewardship programs in healthcare settings. By integrating information technology with healthcare services, hospitals can systematically collect, store, and utilize medical data to improve antibiotic management. Studies have demonstrated that information technology interventions improve antibiotic prescription appropriateness and patient outcomes. The implementation of effective antimicrobial stewardship employs a... -
What Do We Know About Staphylococcus aureus and Oxidative Stress? Resistance, Virulence, New Targets, and Therapeutic Alternatives
Staphylococcus aureus is associated with human infections, being a resistant bacterium involved in serious infections, and its virulence and resistance are linked to oxidative stress. In this study, we review the role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of this bacterium and its influence on immune system evasion, antibiotic resistance, and pharmacological targeting. S. aureus infection generates an intense inflammatory response in the host, evidenced by the activation of pro-inflammatory... -
Solutions to the Dilemma of Antibiotics Use in Livestock and Poultry Farming: Regulation Policy and Alternatives
While the application of antibiotics in livestock production has undeniably propelled the rapid growth of animal husbandry, the escalating crisis of antimicrobial resistance stemming from antibiotic use poses significant threats to global public health and sustainable agricultural development. To address this critical challenge, multifaceted strategies have been implemented through coordinated policy interventions and scientific innovations. This review systematically examines two pivotal... -
Snake Venom Compounds: A New Frontier in the Battle Against Antibiotic-Resistant Infections
The occurrence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria is a serious global health issue, and it emphasizes the need for novel antimicrobial agents. This review explores the potential of snake venom as another alternative strategy against antimicrobial resistance. Snake venoms are complex combinations of bioactive peptides and proteins, including metalloproteases (MPs), serine proteases (SPs), phospholipase A(2) (PLA(2)) enzymes, three-finger toxins (3FTXs), cysteine-rich secretory proteins (CRISPs),... -
Educational interventions and contextual factors for optimising antibiotic prescription in paediatric uncomplicated acute respiratory tract infections in primary care: scoping review of reviews
CONCLUSION: We identified a large number of heterogeneous educational interventions. Combining educational interventions plus another type targeting both parents/caregivers and healthcare professionals, and considering their needs and their context may improve antibiotic prescribing in children. Further research is needed on consultation rate, knowledge, attitudes, and satisfaction outcomes and contextual factors, as well as on the cost-effectiveness of the interventions. -
Natural products as transmission-blocking agents against malaria: a comprehensive review of bioactive compounds and their therapeutic potential
Malaria eradication is hindered by the persistence of transmission stages of Plasmodium falciparum that enable parasite transfer from humans to mosquitoes. Current therapeutic strategies, such as artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) combined with primaquine, are insufficient due to limited efficacy on mature gametocytes and safety concerns in populations with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. This highlights the critical need for innovative, safe, and effective... -
Applying Antimicrobial Strategies in Wound Care Practice: A Review of the Evidence
Antimicrobial resistance is increasing due to an overreliance on antimicrobials to treat and manage infections. Chronic wounds are particularly vulnerable to infections and harbour complex microbial communities, increasing the risk of secondary infections caused by antimicrobial resistant bacteria. Accurate and early diagnosis of infection ensures appropriate treatment interventions and a reduction in the likelihood that antibiotic use is required. Despite this, the overuse of antibiotic... -
Antimicrobial resistance with a focus on antibacterial, antifungal, antimalarial, and antiviral drugs resistance, its threat, global priority pathogens, prevention, and control strategies: a review
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a significant global health threat by diminishing the effectiveness of once-powerful antimicrobial agents, leading to higher rates of illness and death, along with escalating healthcare costs. While bacterial resistance is a primary concern, resistance is also increasing against antifungal, antiparasitic, and antiviral drugs. Many of the last-resort drugs are becoming less effective due to AMR. Projections indicate that by 2050, AMR could cause up to 10... -
The interplay between gut microbiota, antibiotics, and immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with cancer: A narrative review with biological and clinical aspects
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) targeting the programmed cell death-1 (PD-1), programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1), and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) pathways have revolutionized cancer therapy. However, primary and secondary resistance to ICI pose significant challenges. Recent studies underscore the critical role of gut microbiota (GM) in modulating ICI efficacy by shaping host immune responses and regulating the tumor microenvironment (TME). The composition of the GM has... -
Antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: a genetic and physiological perspective
The identification of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection as the primary etiology of gastroduodenal diseases represents a significant advancement in the field of gastroenterology. The management of these diseases has undergone a substantial transformation, and antibiotic treatment is now universally applicable. H. pylori has been the subject of numerous investigations to determine the prevalence of antibiotic resistance. However, many of these studies are limited, particularly regarding... -
A case of hospital-acquired pneumonia associated with Chryseobacterium indologenes infection in a patient with HIV infection and review of the literature
CONCLUSION: C. indologenes infections remain rare but clinically significant in hospitalized patients with immune dysfunction. The pathogen's multidrug resistance profile complicates treatment, necessitating early identification and targeted antimicrobial therapy. Fluoroquinolones, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and cefiderocol may serve as effective treatment options, emphasizing the importance of susceptibility-guided management. -
Prevalence of phenotypic drug resistance profiles and multi-drug-resistant Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter species recovered from clinical specimens in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: The pooled prevalence of Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter species and their antibiotic resistance were alarmingly high in clinical samples in Ethiopia. These findings highlight the crucial need for more antimicrobial surveillance, stronger stewardship programs, and targeted research to combat the growing threat of resistance. Strategic public health policies are required to decrease these pathogens. -
Antimicrobial efflux and biofilms: an interplay leading to emergent resistance evolution
The biofilm mode of growth and drug efflux are both important factors that impede the treatment of bacterial infections with antimicrobials. Decades of work have uncovered the mechanisms involved in both efflux and biofilm-mediated antimicrobial tolerance, but links between these phenomena have only recently been discovered. Novel findings show how efflux impacts global cellular physiology and antibiotic tolerance, underpinned by phenotypic heterogeneity. In addition efflux can mediate... -
Expanding the prevalence of Trichophyton indotineae-associated skin infection by transmission from humans to animals
Infection with Trichophyton indotineae has been considered an important medical issue in recent times due to the rapid ability of this fungus to develop resistance to different antifungals and its widespread distribution across multiple countries. However, increasing cases of antifungal-resistant infections induce changes in the biological activity of fungi, enabling certain dermatophytes such as T. indotineae to infect both animals and humans. This behaviour has certainly had adverse... -
Tiny but Mighty: Small RNAs-The Micromanagers of Bacterial Survival, Virulence, and Host-Pathogen Interactions
Bacterial pathogens have evolved diverse strategies to infect hosts, evade immune responses, and establish successful infections. While the role of transcription factors in bacterial virulence is well documented, emerging evidence highlights the significant contribution of small regulatory RNAs (sRNAs) in bacterial pathogenesis. These sRNAs function as posttranscriptional regulators that fine-tune gene expression, enabling bacteria to adapt rapidly to challenging environments. This review... -
The Global Burden of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria
Background/Objectives: This narrative review provided a broad synthesis of recent epidemiological trends, priority resistance mechanisms, and public health implications of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria. We focused on the most clinically significant MDR pathogens, regional differences in resistance, and the effectiveness of containment strategies. Our goal was to synthesize current knowledge and propose research directions. Methods: Through comprehensive analysis of epidemiological studies,... -
Dichloroacetate and Salinomycin as Therapeutic Agents in Cancer
Cancer is the second leading cause of mortality worldwide. Despite the available treatment options, a majority of cancer patients develop drug resistance, indicating the need for alternative approaches. Repurposed drugs, such as antiglycolytic and anti-microbial agents, have gained substantial attention as potential alternative strategies against different disease pathophysiologies, including lung cancer. To that end, multiple studies have suggested that the antiglycolytic dichloroacetate (DCA)... -
Microbiological and molecular aspects of periodontitis pathogenesis: an infection-induced inflammatory condition
Periodontitis (PD) is the most common oral infectious disease. The primary etiologic cause of the onset and development of PD is dental plaque, which consists of bacterial biofilm domiciled within a complex extracellular mass. In PD patients, there is a progressive breakdown of the periodontal ligament and the alveolar bone. In more advanced stages, tooth loss occurs. The progression of this chronic inflammatory disease involves interactions among numerous microbial pathogens particularly,... -
Limitation of the Lytic Effect of Bacteriophages on Salmonella and Other Enteric Bacterial Pathogens and Approaches to Overcome
Bacteriophages (phages) have emerged as promising agents for combating bacterial pathogens, including nontyphoidal Salmonella enterica (S. enterica), the most common foodborne pathogen worldwide. The emergence of antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) S. enterica poses a severe healthcare issue. Nowadays, many countries worldwide have banned antibiotics for animal feeds or additives, and various strategies have been developed and gained popularity for their potential to address S. enterica infection.... -
Anti-staphylococcal fatty acids: mode of action, bacterial resistance and implications for therapeutic application
Novel strategies to counter multidrug-resistant pathogens such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus are urgently required. The antimicrobial properties of fatty acids (FAs) have long been recognized and offer significant promise as viable alternatives to, or potentiators of, conventional antibiotics. In this review, we examine the interplay between FAs and S. aureus, specifically detailing the underlying molecular mechanisms responsible for FA-mediated inhibition and the counteracting... -
C-reactive protein point-of-care testing to guide antibiotic prescribing for respiratory tract infections
INTRODUCTION: Antimicrobial resistance is strongly correlated with the volume of antibiotics used. Most antibiotics are prescribed in primary care, mostly for respiratory tract infections (RTIs), and are often unneeded. -
Effect of host microenvironment and bacterial lifestyles on antimicrobial sensitivity and implications for susceptibility testing
Bacterial infections remain a major global health issue, with antimicrobial resistance (AMR) worsening the crisis. However, treatment failure can occur even when bacteria show antibiotic susceptibility in diagnostic tests. We explore factors such as phenotypic resilience, bacterial lifestyles such as biofilms, and differences between laboratory tests and real infection sites, highlighting the need for improved platforms to better predict treatment outcomes, and reviewing emerging technologies... -
Antimicrobial resistance in a protracted war setting: a review of the literature from Palestine
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an escalating global health crisis. In war-affected regions, where healthcare systems are already compromised, AMR presents an even greater threat. The occupied Palestinian territories (oPt), subjected to chronic war-like conditions, have experienced extensive fragmentation, de-development, and destruction of healthcare. This review maps the existing knowledge regarding AMR carriage and infection in the oPt. We conducted a scoping review using PubMed, CINAHL,... -
Candida vulturna, the Next Fungal Menace? A Narrative Review
CONCLUSION: Although C. vulturna is still a rare yeast, cases are increasingly reported in tropical regions. The yeast has outbreak potential, in addition to reduced susceptibility to azoles and amphotericin B. Treatment with echinocandins showed favourable outcomes with a low mortality rate. -
Non-antibiotic therapies for multidrug-resistant gastrointestinal infections: an overview of the use of probiotics, natural compounds, and bacteriophages
The worldwide increasing frequency and severity of multidrug-resistant gastrointestinal (MDR-GI) infections not only raises awareness of the debilities of conventional antibiotic treatments but also highlights the demand for alternative interventions. One of these alternatives is probiotics, harmless bacteria that compete with pathogenic species, which have been considered beneficial due to their therapeutic potential since they strengthen the mucosal barrier and modulate the host immune... -
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) in 2025: emerging trends and insights from community and hospital-based respiratory panel analyses-a comprehensive review
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is a significant respiratory pathogen, primarily impacting young, elderly, and immunocompromised populations. While the clinical presentations are similar to those of other respiratory viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza, and SARS-CoV-2, they can still lead to serious complications. The virus primarily transmits via respiratory droplets, with outbreaks peaking during winter and spring. In resource-limited settings, administration of multiplex... -
Antimicrobial Resistance - The 'Real' Pandemic We Are Unaware Of, Yet Nearby
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) represents a persistent and escalating public health crisis, often overlooked despite its severe global impact. Unlike acute infectious diseases, AMR progresses silently but relentlessly, posing long-term threats to health systems worldwide. This review examines the historical evolution and current epidemiology of multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs), emphasizing the global and Korean burden of MDROs. While the development of new antibiotics remains limited,... -
Mechanisms in colistin-resistant superbugs transmissible from veterinary, livestock and animal food products to humans
In the era of antibiotic resistance, where multidrug-resistant (MDR), extensively drug resistant (XDR), and pan-drug resistant (PDR) Gram-negative infections are prevalent, it is crucial to identify the primary sources of antibiotic resistance, understand resistant mechanisms, and develop strategies to combat these mechanisms. The emergence of resistance to last-resort antibiotics like colistin has sparked a war between humanity and resistant bacteria, leaving humanity struggling to find... -
Oral tetracyclines for bone and joint infections: what do we know?
Background and aim: Complex bone and joint infections (BJIs), including prosthetic joint infections (PJIs) and infections associated with osteosynthetic materials, present significant treatment challenges that often require surgical intervention and prolonged antibiotic therapy. In France, the incidence of PJIs in knee and hip arthroplasties ranges from 0.79 % to 2.4 %, with staphylococci being the primary pathogens involved. Recent studies have suggested that oral antibiotic therapy may be as... -
Advancements in AI-driven drug sensitivity testing research
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) constitutes a significant global public health challenge, posing a serious threat to human health. In clinical practice, physicians frequently resort to empirical antibiotic therapy without timely Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST) results. This practice, however, may induce resistance mutations in pathogens due to genetic pressure, thereby complicating infection control efforts. Consequently, the rapid and accurate acquisition of AST results has become... -
Review of respiratory syndromes in poultry: pathogens, prevention, and control measures
Respiratory syndromes (RS) include a variety of diseases that lead to respiratory dysfunction, resulting in significant economic losses for the poultry industry. Infectious agents and unfavourable environmental factors cause these respiratory diseases, and rapid transmission, high morbidity rates, and frequent mixed infections characterise them. The challenge in preventing and treating these diseases arises from the complexity of their triggers and the potential for secondary infections. Current... -
Phytotherapy for acute respiratory tract infections in children: a systematically conducted, comprehensive review
CONCLUSION: Among the phytopharmaceuticals identified by our systematically conducted, comprehensive literature review, EPs 7630 is supported by sufficient evidence to be regarded as an appropriate treatment to reduce the severity and duration of AURTIs and ALRTIs in children. Regarding other phytopharmaceuticals reported in the literature for the treatment of pediatric ARTIs, further research is needed to close existing evidence gaps. -
RND/HAE-1 members in the Pseudomonadota phylum: exploring multidrug resistance
The hydrophobe/amphiphile efflux-1 (HAE-1) family, part of the Resistance-Nodulation-Division (RND) superfamily, plays a critical role in the development of multidrug resistance (MDR) in bacteria. Known for its broad substrate transport capacity, this family of efflux pumps can actively expel a wide range of molecules, including antibiotics, salts, and dyes, thereby reducing the intracellular concentration of toxic substances. These transporters, which form efflux systems, are primarily found in... -
Medicinal plants: bioactive compounds, biological activities, combating multidrug-resistant microorganisms, and human health benefits - a comprehensive review
In recent years, medicinal plants have gained significant attention in modern medicine due to their accessibility, affordability, widespread acceptance, and safety, making herbal remedies highly valued globally. Consequently, ensuring medicinal plants' quality, efficacy, and safety has become a critical concern for developed and developing nations. The emergence of multidrug-resistant microorganisms poses a serious global health threat, particularly in low-income regions, despite significant... -
The application of machine learning in clinical microbiology and infectious diseases
With the development of artificial intelligence(AI) in computer science and statistics, it has been further applied to the medical field. These applications include the management of infectious diseases, in which machine learning has created inroads in clinical microbiology, radiology, genomics, and the analysis of electronic health record data. Especially, the role of machine learning in microbiology has gradually become prominent, and it is used in etiological diagnosis, prediction of... -
Mapping the role of vaccines in combating AMR in the WHO African region: a scoping review and implications for research and policy
CONCLUSION: This review underscores the need for more country-level studies to build evidence on vaccine impact on AMR, including cost-effectiveness studies. Research priorities should include clinical trials with AMR-related endpoints and evaluation of vaccine impact during new vaccine introductions. Strengthening AMR surveillance systems and enhancing collaboration between AMR and vaccination programmes are crucial. The development and review of regulatory frameworks that explicitly address... -
Prevalence of bacterial eye infections and multidrug resistance patterns among eye infection suspected patients in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: In conclusion, the study highlights a high prevalence of bacterial eye infections and multidrug resistance in Ethiopia, with significant regional variation. These findings highlight the urgent need for targeted interventions and antimicrobial stewardship programs to address the growing challenge of antibiotic resistance in Ethiopia. -
Revolutionizing tuberculosis treatment: Breakthroughs, challenges, and hope on the horizon
Tuberculosis (TB), an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), was responsible for the deaths of approximately 1.3 million people in 2022. In addition, 7.5 million new cases of TB have been reported. Present-day treatments require a daily dosing of a multiple-drug regimen for a minimum of six-month, but poor adherence and other factors often lead to treatment failure. Consequently, drug-resistant TB strains have become a growing concern, leading to more... -
A review of antimicrobial resistance challenges in Nigeria: The need for a one health approach
The discovery of penicillin and other antibiotics has revolutionized modern medicine. However, overreliance on antibiotics has led to a global antimicrobial resistance (AMR) crisis, jeopardizing progress made over the past decades. Antimicrobial resistance poses a critical public health challenge, affecting humans, animals, and the environment. The AMR challenge is particularly dire in Nigeria owing to the extensive antibiotic use across various sectors and ineffective antimicrobial stewardship... -
Unlocking the power of antimicrobial peptides: advances in production, optimization, and therapeutics
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are critical effectors of innate immunity, presenting a compelling alternative to conventional antibiotics amidst escalating antimicrobial resistance. Their broad-spectrum efficacy and inherent low resistance development are countered by production challenges, including limited yields and proteolytic degradation, which restrict their clinical translation. While chemical synthesis offers precise structural control, it is often prohibitively expensive and complex for... -
Correction: Lee et al. Prioritization of Critical Factors for Surveillance of the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15209
The journal's Editorial Office and Editorial Board are jointly issuing a resolution and removal of the Journal Notice linked to this article [...]. -
Lactic Acid Bacteria Bacteriocins: Safe and Effective Antimicrobial Agents
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are major contributors to food spoilage, animal diseases, and the emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria in healthcare, highlighting the urgent need for effective treatments. Bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) have gained attention for their non-toxic nature and strong antimicrobial properties. LAB-derived bacteriocins have been successfully applied in food preservation and are classified by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as... -
Hypocrellin-Mediated PDT: A Systematic Review of Its Efficacy, Applications, and Outcomes
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a light-activated treatment that generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) to induce microbial cell death. As resistance to traditional antibiotics intensifies globally, PDT has emerged as a promising alternative or adjunctive antimicrobial strategy. Among various photosensitizers, Hypocrellin, a perylenequinone compound, has shown high ROS yield and broad-spectrum activity against bacteria and fungi. This systematic review evaluated the efficacy, safety, and... -
The Impact of Plant-Derived Polyphenols on Combating Efflux-Mediated Antibiotic Resistance
The global healthcare system is increasingly challenged by the rising prevalence of multidrug-resistant bacteria and the limited therapeutic options for related infections. Efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance represents a significant obstacle, primarily due to the absence of drugs specifically designed to target bacterial efflux pumps. Recent research has identified polyphenols, a broad class of plant-derived organic compounds, as potential inhibitors of efflux pump activity. This review... -
Assessing Salmonella Typhi Pathogenicity and Prevention: The Crucial Role of Vaccination in Combating Typhoid Fever
Enteric fever is caused by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S. Typhi) and Salmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi (S. Paratyphi) A, B, and C. Globally, an estimated 11 to 21 million cases of typhoid and paratyphoid fever occur annually, with approximately 130,000-160,000 deaths, most of which are reported in South/Southeast Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. The antibiotic susceptibility of S. Typhi strains varies between countries within broad limits, from 3% to 97% for ampicillin, 9% to 95% for... -
Hallmarks of Bacterial Vaginosis
Background: Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is considered the most common cause of vaginal discharge, which is related to several public health issues, such as an increased risk for sexually transmitted infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, pregnancy-related problems such as abortion, stillbirth or premature birth, and tubal factor infertility. BV is not considered an infection but an imbalance in the vaginal microbiota, characterized by a substitution of the normal Lactobacilli flora by anaerobe.... -
Global knowledge, attitudes, and practices towards antimicrobial resistance among healthcare workers: a systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: The findings underscore the need for targeted interventions to enhance the knowledge, attitudes, and practices of HCWs regarding AMR. Priority should be given to designing and implementing robust training programs tailored to the specific needs of HCWs in resource-constrained settings. Strengthening AMR-related education and practice among HCWs is crucial for combating the global AMR crisis effectively. -
Reviewing the complexities of bacterial biocide susceptibility and in vitro biocide adaptation methodologies
Decreased bacterial susceptibility to biocides raises concerns due to their influences on antibiotic resistance. The lack of standardized breakpoints, established methods, and consistent terminology complicates this research. This review summarizes techniques for studying biocide resistance mechanisms, susceptibility testing, and in-vitro adaptation methods, highlighting their benefits and limitations. Here, the challenges in studying biocide susceptibility and the need for standardized... -
Antimicrobial resistance in community-acquired enteric pathogens among children aged 10-years in low-and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: Our results shed light on drug-resistant enteric bacterial pathogens in young children, providing evidence that CESS pathogens are becoming increasingly resistant to clinically important antimicrobials. Regional differences in resistance patterns between these community isolates highlight the need for strong national and regional surveillance to detect regional variations and inform treatment and appropriate antibiotic stewardship programs. The limitations of our findings include... -
Prevalence of bedaquiline resistance in patients with drug-resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSIONS: Our findings highlight an increasing trend in acquired resistance to BDQ, offering critical insights for managing MDR-TB. The application of whole-genome sequencing shows promise for advancing understanding of drug resistance mechanisms in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. -
Recent Advances in Therapeutic Peptides: Innovations and Applications in Treating Infections and Diseases
Peptides have become a powerful frontier in modern medicine, offering a promising therapeutic solution for various diseases and advancing rapidly in pharmaceutical development. These small amino acid chains, with their innovative design, have attracted significant attention due to their versatility and high receptor specificity, which minimizes off-target effects, along with enhanced therapeutic efficacy, biodegradability, low toxicity, and minimal immunogenicity. They are being explored for use... -
Antibiotic resistance and preventive strategies in foodborne pathogenic bacteria: a comprehensive review
Antibiotic resistance in foodborne bacteria poses a substantial global health challenge. Reports indicate that antibiotic overuse in middle-class and low-income countries is a significant factor in the ever-increasing resistance. Resistance mechanisms have developed through enzymatic hydrolysis, reduced membrane permeability, efflux pumps, and target site mutations. Preventive measures like proper hygiene and safe food preparation, vaccination, antibiotic stewardship and surveillance,... -
Prevalence, trends, and molecular insights into colistin resistance among gram-negative bacteria in Egypt: a systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: In Egypt, BMD testing identified colistin resistance in 9% of Gram-negative bacteria, increasing to 31% in carbapenem-resistant isolates. This higher resistance in carbapenem-resistant strains suggests stronger selective pressure from frequent colistin use. Additionally, colistin resistance has shown a rising trend over time, likely driven by increased usage and the spread of plasmid-mediated resistance. These findings underscore the urgent need for strict antimicrobial stewardship... -
Strengthening global health security through antimicrobial resistance control: Insights from Saudi Arabia
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a significant threat to global health security, and Saudi Arabia plays a key role in addressing this challenge. This review highlights Saudi Arabia's National Action Plan, which focuses on improving data collection, monitoring AMR trends, and promoting the responsible use of antimicrobials in human and veterinary medicine. While the Kingdom has shown leadership in regional AMR control efforts, recent data indicate rising resistance rates among key pathogens,... -
A scoping review of worldwide guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection
CONCLUSION: Current global Helicobacter pylori management guidelines share foundational consensus, yet exhibit regional variations in diagnostic criteria, eradication indications, and therapeutic regimens due to context-specific epidemiological, socioeconomic, and antimicrobial resistance profiles. Clinical practice should prioritize regionally tailored approaches, integrating local guidelines while maintaining awareness of international recommendations to optimize decision-making. Moreover,... -
Exploring heme and iron acquisition strategies of Porphyromonas gingivalis-current facts and hypotheses
Iron and heme are crucial for pathogenic bacteria living in the human host but are not available in free form due to their binding by iron- and heme-sequestering proteins. Porphyromonas gingivalis causes dysbiosis in the oral microbiome and is considered a keystone pathogen in the onset and progression of periodontal diseases. Its ability to infect and multiply in host cells and its presence in distant tissues and fluids highlights its pathogenic versatility and explains the relationship between... -
Global patterns of antibiotic resistance in group B Streptococcus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: This study emphasizes the growing issue of antibiotic resistance in GBS strains. Notable resistance to older and newer antibiotics, increasing resistance over time, regional disparities, and methodological variations are noted. Rising resistance trends for multiple antibiotics underscore the urgent need for global surveillance and improved antibiotic stewardship. -
Evaluation of the Adjunctive Effect of Photodynamic Therapy for the Treatment of Residual Periodontal Pockets: A Systematic Review
CONCLUSIONS: Photodynamic therapy in combination with scaling and root planing may result in modest reductions in residual periodontal pocket depth levels and improvements in clinical attachment levels. The use of PDT in periodontal maintenance can reduce or eliminate the need for periodontal surgery, which may be more invasive and lead to a longer recovery time. -
Progress in the classification, optimization, activity, and application of antimicrobial peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) come from various sources and exhibit unique antimicrobial properties. Their rapid action, effectiveness, and resistance to resistance development make them promising alternatives to combat antibiotic resistance. In addition to its excellent antibacterial properties, AMPs have superior immunomodulatory, antitumor, and antiviral activities. In recent years, the demand for AMPs has continued to increase in many fields, especially in the medical field, and the... -
Probing and manipulating the gut microbiome with chemistry and chemical tools
The human gut microbiome represents an extended "second genome" harbouring about 10^(15) microbes containing >100 times the number of genes as the host. States of health and disease are largely mediated by host-microbial metabolic interplay, and the microbiome composition also underlies the differential responses to chemotherapeutic agents between people. Chemical information will be the key to tackle this complexity and discover specific gut microbiome metabolism for creating more personalised... -
Exploring the accuracy of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay in detecting lymph node tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
CONCLUSION: Xpert MTB/RIF demonstrated excellent accuracy for diagnosing LNTB and rifampicin resistance, with FNA samples outperforming tissue samples acquired through biopsy and CRS as superior to culture standards. -
Chronicling the Journey of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Introduction in India
CONCLUSIONS: The phased rollout was an ambitious effort by the MoHFW, which was particularly challenging given the overlap with the COVID-19 pandemic. Despite these hurdles, the MoHFW, along with strong collaboration from development partners and stakeholders, successfully navigated the complex rollout. Future studies on the role of PCVs in reducing antibiotic resistance and the economic benefits of PCV introduction could help policymakers sustain funding and prioritize vaccine procurement... -
Disarming Staphylococcus aureus: Review of Strategies Combating This Resilient Pathogen by Targeting Its Virulence
Staphylococcus aureus is a formidable pathogen notorious for its antibiotic resistance and diverse virulence mechanisms, including toxin production, biofilm formation, and immune evasion. This article explores innovative anti-virulence strategies to disarm S. aureus by targeting critical virulence factors without exerting bactericidal pressure. Key approaches include inhibiting adhesion and biofilm formation, neutralizing toxins, disrupting quorum sensing (e.g., Agr system inhibitors), and... -
From Microbial Ecology to Clinical Challenges: The Respiratory Microbiome's Role in Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance represents a growing public health threat, with airborne drug-resistant strains being especially alarming due to their ease of transmission and association with severe respiratory infections. The respiratory microbiome plays a pivotal role in maintaining respiratory health, influencing the dynamics of antibiotic resistance among airborne pathogenic microorganisms. In this context, this review proposes the exploration of the complex interplay between the respiratory... -
Targeting Siderophore Biosynthesis to Thwart Microbial Growth
The growing threat of antibiotic resistance has made treating bacterial and fungal infections increasingly difficult. With the discovery of new antibiotics slowing down, alternative strategies are urgently needed. Siderophores, small iron-chelating molecules produced by microorganisms, play a crucial role in iron acquisition and serve as virulence factors in many pathogens. Because iron is essential for microbial survival, targeting siderophore biosynthesis and transport presents a promising... -
Recent Macrolide Resistance Pattern of Mycoplasma Pneumonia in the World: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
CONCLUSION: While the prevalence of macrolide-resistant M. pneumonia is quite low in America, it is a great dilemma in East Asia and the low prevalence in most countries could be underestimated. This study revealed an increasing trend in macrolide resistance. Indiscriminate and improper use of macrolides may be a warning in this regard. -
Current methods in the diagnosis of invasive meningococcal disease
Invasive meningococcal disease (IMD) remains a significant health concern due to its global distribution, potential for epidemic spread, unpredictable nature, rapid progression, and high mortality rates or permanent sequelae. The global elimination of meningococcal illness via immunization is a primary objective of the World Health Organization's strategy to defeat meningitis by 2030. Timely recognition of meningococcal infection and immediate, precise, and specific identification of Neisseria... -
Indole signaling in Escherichia coli: a target for antivirulence therapy?
Pathogenic Escherichia coli are a major cause of infections in both humans and animals, leading to conditions such as severe diarrheal diseases, urinary tract infections, enteritis, and septicemia. To combat bacterial infections, antibiotics are widely utilized. However, the extensive and inappropriate use of antibiotics has fueled the development and spread of antibiotic resistance, posing a significant challenge to the effective treatment of E. coli. There is consequently an urgent need to... -
Research progress in silver ion tolerance mechanisms of Escherichia coli
Due to the wide application of silver-containing dressings and silver-coated medical devices in clinical treatment; the extensive use of antibacterial agents and heavy metal agents in feed factories, Escherichia coli has formed the tolerance to silver ions. To systematically understand the known silver ion resistance mechanisms of E. coli, this article reviews the complex regulatory network and various physiological mechanisms of silver ion tolerance in E. coli, including the regulation of outer... -
Multidrug resistance of Helicobacter pylori and its impact on the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases and countermeasures
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that can cause chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and other gastrointestinal diseases. The World Health Organization has classified H. pylori as a group Ⅰ carcinogen. Antibiotics are the primary clinical approach for eradicating H. pylori. However, incomplete eradication of H. pylori by antibiotics can lead to persistent infection, which is a major risk factor for the high incidence of gastric cancer. The widespread use of antibiotics has led to the emergence of... -
Identifying context-specific determinants to inform improvement of antimicrobial stewardship implementation in healthcare facilities in Asia: results from a scoping review and web-based survey among local experts
International guidelines are available for the assessment and improvement of antimicrobial stewardship (AMS) programmes: an important strategy to address the escalating global antimicrobial resistance problem. However, existing AMS assessment tools lack contextual specificity for resource-limited settings, leading to limited applicability in Asia. This project aimed to identify relevant themes from current guidance documents to help develop a context-specific assessment tool that can be applied... -
Antimicrobial resistance among children in Southeast Asia: a systematic review
CONCLUSIONS: There are very high rates of AMR in pathogens isolated from children with common infectious illnesses in Southeast Asia. However, published data available are of variable quality and are heavily weighted towards South Asian countries (India, Nepal and Bangladesh), limiting the generalisability of these findings and highlighting the need for enhanced clinical surveillance networks to improve the surveillance within this populous and high-burden region. -
Gut Microbiota and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Metabolic Products and Immunotherapy Modulation
CONCLUSIONS: The focus is on translating these insights into personalized medicine to optimize ICIs responses and improve HCC treatment outcomes.



